Movies play an essential part in our lives.
While you can watch movies in the comfort of your own home, nothing beats the experience of going to the cinema and watching blockbuster movies on the big screen.
Cinemas display larger than life movie images with the use of Projectors.
What is a projector used for?
A projector is a device that has the ability to project an image (or moving images) onto a screen (or plain surface). It’s main purpose is to recreate images at a larger scale compared to the limitations of television, laptop, computer screens.
But, the projector has many other uses than just displaying movies at the cinema. This article will discuss other applications where a projector can be used.
Also, you can recreate the cinema experience in the comfort of your own home with the aid of a projector.
Deeper look at the projector
Before we dive into the different applications a projector is used for, let’s take a deeper look at the projector and its working principle.
If you are not interested in this section you can just skip to the ‘Different uses of projector’ further in this article.
Brief history of the projector
The projector dates back all the way to the early 17th century where it was known as a ‘Magic lantern’. A man named Christian Huygens is known for being its inventor.
Crucial optical components used for projections in the magic lantern such as lenses and prisms are still used in modern day projectors.
Then came the era of Cinema!
Projectors play an important role in the film industry to project images at large scale.
The first known projector was the Zoopraxisciope, created by Eadweard Muybridge in 1879. The Zoopraxiscope achieved motion by projecting images at a rapid pace from rotating glass disks.
However, the more successful movie projector was created by the Lumiere Brothers based on the work of French inventor Leon Bouly.
All these projectors mentioned above were analog. In the early 2000s they started getting replaced by digital versions which proved to be more advantageous compared to their analog counterparts.
What does the projector do
The projector is an output device and as its name suggests, has the ability to ‘project’ images or video onto surfaces like a projector screen or wall.
To project content (such as an image or video) the projector will need to be connected to a host device such as a computer, due to the fact that it does not have the ability to produce its own content.
The computer sends content to the projector which it then reproduces at a larger scale.
Since the analog projector is outdated, from now on when I refer to the projector, it will be of the digital kind.
Different parts of a projector
There isn’t one particular component that makes the projector. There is a list of parts that help it achieve its end goal of projecting an image.
Removing any of these parts will render the project useless. So each component plays a pivotal role.
Below is a list of the different parts that make up a projector, and a small description of what each one does.
Lens
The first part of the projector is the Lens. The lens is responsible for projecting images onto a surface such as a screen.
Nowadays, lenses have the ability to zoom.
This means you can make an image larger or smaller without actually having to move the projector from its current fixed location.
Projection lamp
The projection lamp is a light source which aids in the process of projecting an image.
As you can imagine, the brightness of the projected image relies heavily on the power the projection lamp is capable of outputting.
A Projection lamp can either be a Halogen bulb (most common in older projectors) or Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs).
HDMI connectors
High Definition Multimedia Interface (or HDMI), is the newest and most common way of transferring high definition Audio and Video over a single cable.
HDMI is now utilised by most (if not all) current digital projectors. So, every projector has HDMI ports, which media devices such as computers, DVD players, gaming consoles,etc, can be connected to.
Power input
Just like any other electronic device, the projector needs electricity to operate. The power input is where you can plug in a power cable, which then gets connected to a power socket to power the projector.
Control Panel
Whether it is physical buttons, or a LCD touchscreen, the projector will have a control panel where you can choose different options and settings. Things, like play, pause, brightness level, contrast level, etc.
Remote Control
Having to get up constantly to press pause, play or change settings on the projector is inevitably going to get very frustrating. That’s where the projector’s remote control solves the problem. Now you interact with the projector without having to leave the comfort of your seat.
LAN
Most modern projectors have Wi-fi capability. But, wi-fi cannot always be reliable. So, having a LAN input can provide a means of wired internet connection.
FAN
Fans are crucial components in many electronic devices. They help cool down components that get hot.
The fan in the projector is no different. Since a light source is used to project images inside a projector, temperatures are going to rise. The fan can maintain an optimum temperature for the projector to operate within.
Different applications of a projector and what its used for 00
Ok, let’s take a look at what the projector is used for.
As we saw earlier in the ‘what does the projector do’ section, the projector has the task of taking media such as an image, or series of images (video) and projecting it onto a surface at a larger scale.
So, with that in mind, let’s take a look at the different applications of a projector.
Application #1 of projector: Home theater (cinema)
Let’s start with the most obvious application, one which you might already be familiar with, a Home theatre (or cinema) application.
Nothing beats the experience of going to the cinemas to watch a blockbuster film on the big screen.
But, nowadays, the price of a ticket to go see a movie in the cinema can be quite hefty. Going on a regular basis isn’t the best option.
However, this is not the end of the story!
With the help of a projector, you can recreate the cinema experience right in the comfort of your living room.
Below are some other things you might need to create the best home cinema experience:
- A projector screen
- Comfy sofas/couches
- Surround sound
- A dark room (to avoid glare on the screen)
- and, Popcorn of course!
Application #2 of projector: Business Presentations
Ah, business meetings!
They can be quite a pain right?!
However, meetings are an essential part of every business.
They help inform, educate, motivate and persuade people inside and outside of the business about sales, the current status of the company, plans for the future, and so much more.
Printing multiple reports (which is a waste of paper), or having people crowd around a single computer, or laptop is not the most efficient or effective way of presenting information.
The best option here is to use a projector along with a software such as PowerPoint Presentation, to better collate and present your information at a larger scale with more efficiency and effectiveness.

Application #3 of projector: Classroom teaching
Whether you like it or not, schools are starting to go the digital route.
Children are getting their own laptops which are replacing books.
Another aspect of the classroom that is changing is how teachers present information to their classes.
Traditionally, chalkboards are used by teachers to write on to convey new information and show examples as well.
While this is not a bad way of conveying information, it does have some downsides.
The clarity of the information presented is dependent on the teacher’s ability to write neatly. If they have bad handwriting, it might make it more difficult for the students to understand and copy the information.
Also, a lot of time is spent writing which places physical stress on the teacher, and eats up a lot of teaching time.
A projector can be used to display information that is clear to read. As you also have the option of zooming in and out, children sitting further back in the classroom will not have any issues.
Using a projector also means that the teacher can pre plan a class lesson the day before which means that information can be presented instantaneously the day of the lesson.
This means the teacher can concentrate more on teaching the information at hand rather than writing it down.
The class lesson will also be saved as a digital file which can be reused for future lessons. Also, if any child missed the lesson, they can get their hands on the lesson, whereas a chalkboard would have to be erased.
Projectors are also very common in colleges (universities) to teach a large group of students.
Application #4 of projector: Multiplayer gaming
I spent a lot of time when I was younger playing multiplayer games with my friends.
Games such as Super Mario Kart, Halo, Crash Team Racing, and many others.
With these games you could have up to 8 players (if you had the right amount of controllers).
If you have ever played a multiplayer game with 4 or more players, you know that if the screen is split between the number of players playing (for certain multiplayer games, like racing or first person shooters etc).
This means that playing on a normal television screen (even though they are quite big these days), with so many players reduces the size of each player’s personal screen, making the gaming experience a bit harder.
A projector used for multiplayer gaming would mean that you can expand the screen size for each player while maintaining quality and enhancing the gaming experience.
Application #5 of projector: Art
You might be wondering, how on earth can a projector be used for Art?!
Well, you would be surprised!
Technology is playing a big part in the emergence of the ever growing sub-genre of Digital Art. The projector is one of those technologies used prominently in many Digital Art installations.
It can be used to cast artwork onto walls, temporary installations, buildings, and many other surfaces.
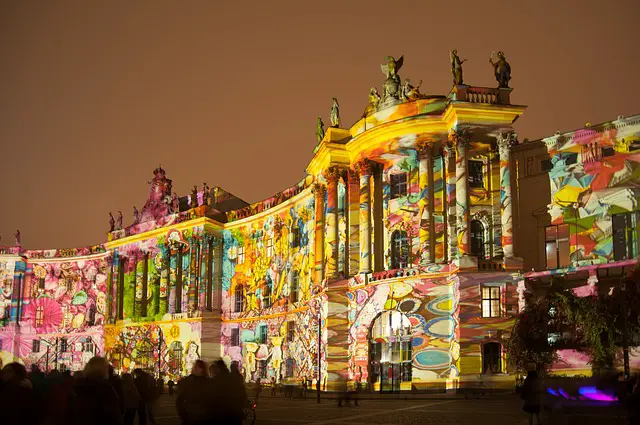

It also proves handy for painting murals on large surfaces.
The artist can cast the image of the mural they are wanting to paint onto a wall, so that they can then plan and have guidelines of where to paint.
Application #6 of projector: Slideshows
There are many milestones in our lives that we celebrate on a big scale.
Nothing more like birthday milestones; Sweet 16, 21st, 30th, 50th etc.
A projector can be a great way to display a slideshow of photos of the birthday boy/girl.
It’s especially good if they are funny photos of them (so make sure to save funny photos of your friends, children, loved ones, etc for a potential future slideshow).
Different types of projector and what they are used for
There isn’t one specific type of projector that is used for all applications mentioned above.
Projectors do vary in different characteristics that might make one more suitable for a particular application compared to the other.
Below are the 4 most common types of projector used (again these are digital projectors);
- DLP (Digital Light Processing)
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
- LED (Light Emitting Diode)
- LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon)
Let’s take a quick look at each type of projector and what type of application each is best suited to be used for.
Digital Light Processing (DLP) Projectors
This type of projector uses a series of tiny mirrors which reflect light onto a screen.
There is a colour wheel (or colour filter) that rotates in order to generate an array of colours. The colors on the wheel are usually Red, Green and Blue, as these colours can be combined to produce many other color variations.
Advantages of DLP Projectors
- Vibrant colours
- High Contrast
- Sharper images with minimal space between pixels
- Minimal light loss while achieving maximum light output
- Deeper Blacks
Disadvantages of DLP Projectors
- Rainbow effect
- Pixels are limited
- Lower brightness
- Random flashes across screen
Applications of DLP Projectors
- Business meetings, conferences, seminars
- Home cinemas
- Gaming
- Schools and Colleges
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Projectors
LCD projectors utilise the same technology prevalent in television and computer screens.
This type of projector uses three LCD panels which project an image. Just like the DLP projector, the three primary colours Red, Blue, and Green, are used to generate a myriad of colours.
Advantages of LCD Projectors
- More light efficient compared to DLP projectors
- Brighter images
- Colours vibrant in brightly lit rooms
- Sharp and focused image
Disadvantages of LCD Projectors
- Projector is heavy and inconvenient to move around
- Dead pixels may arise over time
- Short lifespan as well as being expensive
Applications of LCD Projectors
- Schools and colleges
- Business meetings, conferences, seminars
- Home cinemas
Light Emitting Diodes (LED) Projectors
Next up is LED projectors.
As mentioned earlier, the project has a projection lamp, which is a light source which aids in projecting images.
With this type of projector, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) lamp is used.
LED lamps are ideal as they produce very little heat compared to incandescent light bulbs, making them very efficient and also helps increase their lifespan.
Advantages of LED Projectors
- More efficient to other projectors that use incandescent light bulbs
- Can produce a wide variety of color without the need of a color filter
- Compact
- Faster setup time
- Longer lamp lifespan
Disadvantages of LED Projectors
- Can be quite expensive
- Require an optimum temperature to operate effectively
- Blue light pollution
Applications of LED Projectors
- Business meetings, seminars, conferences
- Home cinemas
- Education (classrooms, colleges)
Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCOS) Projectors
Last, but not least, is the Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCOS) projector.
This type of projector uses similar technology to a LCD projector.
However, rather than just passing through LCD cells, the red, blue and green components of the divided light reflect off a shiny surface behind a cell array.
It uses three LCOS chips to divide the white light into red, blue and green components.
Advantages of LCOS Projectors
- High resolution
- Smoother pixel edges
- Natural images
Disadvantages of LCOS Projectors
- Low contrast ratio
- Bad in ambient lighting
- Short lamp lifespan
Applications of LCOS Projectors
- Near to eye viewing systems
- Optical beam steering
- Micro projectors
- Holographic projectors
Benefits of a projector
The projector has many different applications it is used for because it has many benefits, some of which are listed below;
- Larger images (while maintaining quality)
- Recreate cinema experience
- Deliver presentations to large group of people (classrooms, business meetings, etc)
- Eye comfort (Your eyes will feel more comfortable looking at a projected image)
- Compact
- Portable
Final thoughts
So, the main purpose of a projector is to create a large scale image or video.
But, while they are most commonly used in cinemas, and home cinemas for watching movies, they have plenty of other applications when they are used.
They are great for delivering information to the masses in a clear, and concise manner. But, it comes down to your imagination and creativity as you saw with its uses in the art scene as well.
The possibilities are endless!