Diodes are common semiconducting electronic components used in circuits to allow current to only flow in one direction.
Zener diodes are a type of diode with the ability to allow current to flow in one direction, as well as allowing a large reverse current to flow at a critical reverse voltage.
Electronic components all heat up at a certain point.
You might have encountered this with your electronic devices like a laptop or smartphone when you have been using it for extended periods of time.
So, do zener diodes get hot? Yes, zener diodes do get hot. Zener diodes, like other electronic components, have a maximum power rating. Exceeding this power rating will cause the zener diode to expel excess energy in the form of heat and get hot.
This article shall delve deeper into why zener diodes get hot.
Keep reading to learn more.
Why do zener diodes get hot?
So, why exactly do zener diodes get hot?
To answer this question, we first have to take a couple steps back and look at some fundamental theories which include energy, power ratings, and current.
Don’t worry, it will be brief.
Energy
Let’s start with energy.
The First Law Of Thermodynamics states; “Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another”.
The total amount of energy in the world remains constant.
So, for example, if you are seated at this moment reading this article, you have Potential Energy. When you get up to maybe go get a new cup of coffee, that potential energy is converted to Kinetic Energy.
Forms of potential energy include;
- Chemical
- Nuclear
- Elastic
- Gravitational
Forms of kinetic energy include;
- Mechanical
- Electrical
- Thermal
- Sound
- Light
Later we shall see how this applies to zener diodes.
Power ratings
All electrical/electronic devices and components have Power Ratings.
This defines the maximum allowable power that the device can be subjected to. If you exceed this limit you pose the threat of permanent damage to the device or component.
Electrical appliances will have a label indicating their power rating, while electrical and electronic components will have this information in their datasheets.
Power rating is a product of a device/components voltage and current rating.
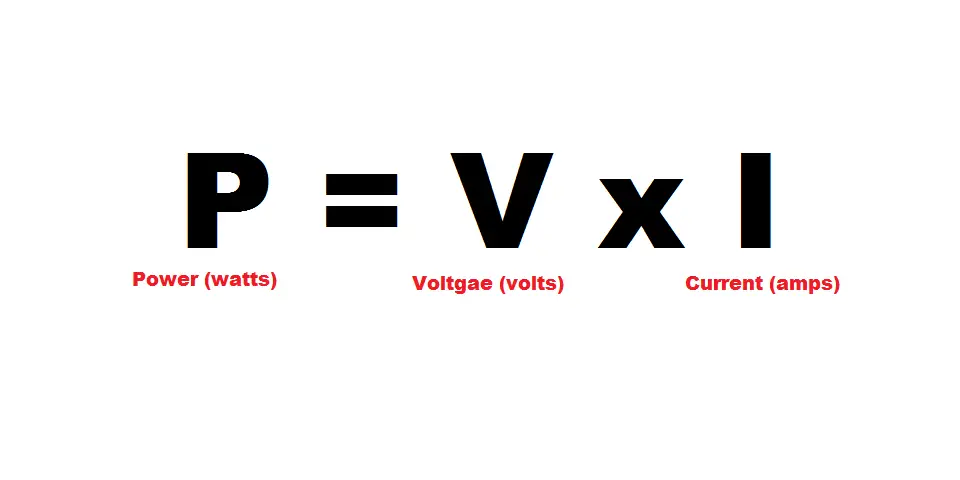
The equation above shows us that power shares a directly proportional relationship with voltage and current.
This means that increasing either voltage or current will increase power.
Power ratings have the standard international unit of Watts (W).
What happens inside the zener diode when it gets hot?
But why is power rating important?
To get a clear picture of this, let’s take a look inside a cable and see what happens. This same concept applies to all other devices and components as well, but the cable is an easier example.
Also, just like components, cables have power ratings.
Current is the lifeblood that runs through all electrical/electronic circuits and components. Without current the electrical and electronic world would stop still.
It is defined as the flow of electrons past a given point in a circuit.
Ampere (Amp), is the unit of measurement that tells us the number of electrons passing this given point. The higher the current, the higher the number of electrons, and vice versa.
Ok, let’s take a look at a cable at the flow of electrons through it.
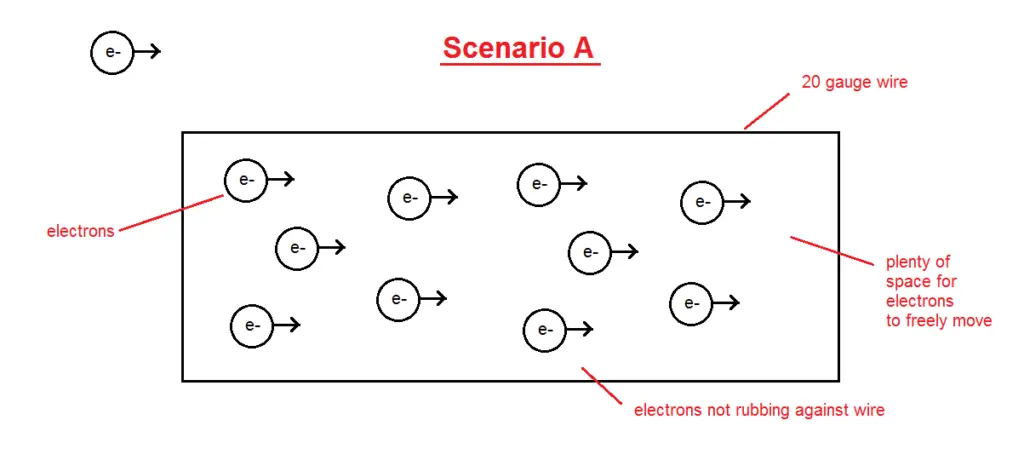
The image above shows us a sliced up view of a cable. Let’s imagine that this cable is rated at 5 watts.
In this scenario, the cable is operating within its power ratings, so the amount of current (electrons) flowing through the wire is an amount that is within the cable’s capability.
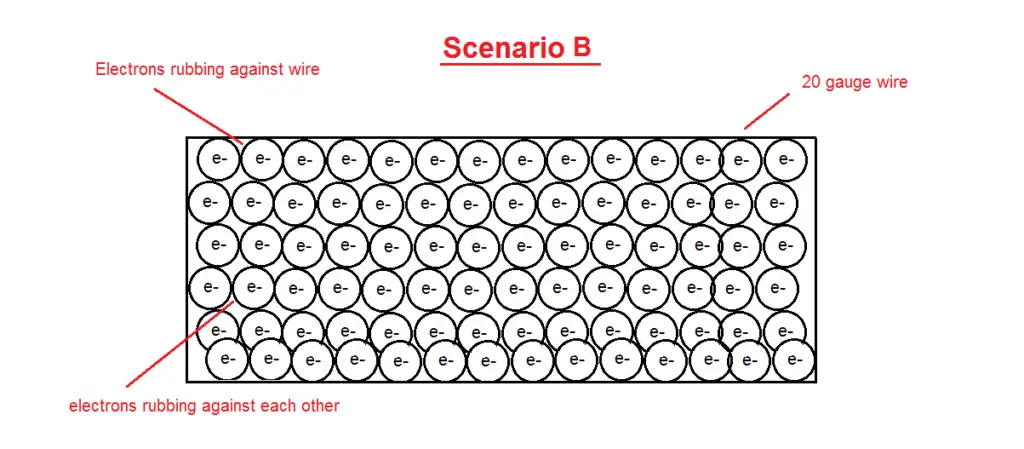
Now, if we increase the amount of current (electrons) drastically, we increase the power through the cable ( as current is directly proportional to power).
This causes a bottleneck effect within the cable as we can see in the image above.
Here electrons cannot freely move, and bump into each other. As we learnt earlier, energy cannot be created or destroyed.
As electrons move and bump into each other (kinetic energy), they cause friction and release energy in the form of heat.
So why do zener diodes get hot? Because an increase in current through the zener diode causes an increase in power. When this power exceeds the zener diode’s power rating, energy is released in the form of heat as electrons flowing through the zener diode bump into each other.
Can a zener diode get hot under normal conditions?
But, will zener diodes get hot if you stay within the power ratings?
Zener diodes, like other electronic components, will warm up to a certain extent even when they are operated under their normal power ratings.
This is because heat will still be released as electrons bump into each other. But, the frequency of collisions will be far less compared to when excess current is flowing through the zener diode.
So, under these normal conditions (and assuming they are wired correctly as well), zener diodes will not get hot.
And here hot is defined as unusually high temperatures (outside the maximum temperature that the zener diode should be subjected to).
Is there a certain power rating at which a zener diode gets hot?
Zener Diodes come in a range of sizes, packaging (through hole, SMD), voltage, current and power ratings. This is so that you have the option of selecting the right one for a certain application.
So there won’t be a specific number of voltage, current, or power rating, at which all zener diodes get hot. Every zener diode will have been tested accordingly and have its own unique maximum power rating.
And as we learnt earlier, getting near to, or exceeding the power rating will cause the zener diode to get hot.
Also, the size of the zener diode will play a big part in how much current it can handle.The bigger its size, the more current it can handle and therefore it will have a higher power rating.
To find the power rating information of zener diodes you will have to look at its datasheet which is provided by the manufacturer (this can be found online).
What happens when zener diodes get hot?
Maximum power ratings are there for a reason.
They help us stay within the limits of the components to protect them. Exceeding this power rating will cause excess current which leads to it getting hot.
But, what happens when it gets hot?
There are a couple of things that can happen.
The first occurrence is a phenomenon known as Thermal Runaway, which describes a scenario where an increase in temperature dissipates energy (in the form of heat), further causing an increase in temperature.
This will cause the zener to get hotter.
Next, once the temperature has reached a level which the casing (structure) of the zener diode cannot handle, it is going to rupture which could lead to the diode smoking.
Or, in a worst case scenario, a small explosion.
The zener diode is now permanently damaged and will need to be replaced.
How to avoid zener diodes getting hot
Whether it be with zener diodes, or any other aspect of life, accidents are going to occur. But, being prepared is the best way to minimize and reduce the chances of accidents occurring.
So what is a good way of avoiding zener diodes overheating?
The first step is to know the maximum power of the circuit/application where the zener diode will be used.
Next is to choose a zener diode that has power ratings which matches, or is slightly higher than the circuit’s power rating.
The rule of thumb is to choose a rating slightly higher to give it some allowance.
Always check the datasheet of the zener diode you are purchasing and make sure to check its power, voltage and current ratings.
Bigger zener diodes will be dealing with higher currents and therefore are going to get hot (which is normal).
In this scenario you will need to use a Heat-sink, which is a component used to dissipate excessive heat.